Montessori System
The Montessori system was developed by Dr Maria Montessori, it is a child centric method of education that emphasizes on collaboration, independence and discovery.
Montessori education was founded on the belief that a child’s education should be constructed to develop all aspects of a child: social, emotional, physical and academic. The first six years of life are very crucial because it is marked by tremendous physical and psychological growth, exploration and development.
Montessori classrooms are peculiar yet beautiful. There is a unique essence to it, when we see children working independently and in groups, with scientifically designed learning materials. They are deeply engaged in their work and respectful of themselves and their surroundings. Montessori education is student-led and self-paced but guided, assessed, and enriched by knowledgeable, trained and caring teachers.
Children have the freedom and support to question, enquire and discover. Thus, Montessori students grow up to be confident, enthusiastic, and self-directed learners, accountable for themselves and their community. They think critically, work collaboratively, and act boldly and with integrity. What better can we wish for our children, other than Montessori education?
Rather than simply filling children with facts, the goal of early childhood education should be to activate the child’s own natural desire to learn
Components of Montessori Education:
- Mixed-age groups – Having children of different ages together in the classroom mimics the real world, teaching students how to get along with people of different ages and interests. Younger students naturally learn more from their older peers. A multi-age classroom is designed to create natural opportunities for independence, citizenship, and accountability.
- Student choice of work - Individual students follow their own curiosity at their own pace to meet individualized learning goals. Children embrace multi-sensory learning and passionate inquiry. Sometimes the teacher will give students a choice among a set of hands-on activities. These activities introduce or reinforce concepts and skills a teacher selects based on the students' ages and needs. Among the benefits of this approach, teachers can design activities that match each child's age and ability as well.
- Uninterrupted work cycles to engage deeply in activities - Our goal is to give the children, the time they need to explore and understand the world around them. Children are respectful or each other and their work, thus they function as a cohesive unit and each one takes the time, they need to fully understand each concept and meet individualized learning goals.
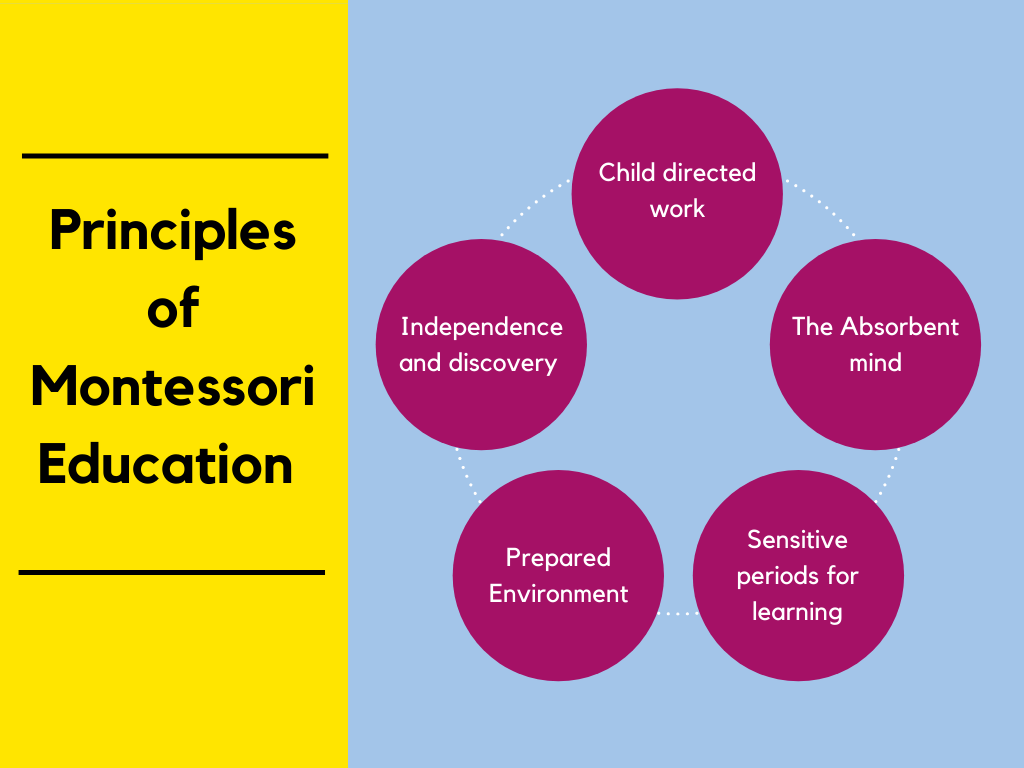
The five principles of Montessori education:
- Child directed work - Each day Montessori teachers give their students some choice of activity. Students are given the chance to choose an activity that captures their personal interest or attention and then, once an activity has been chosen, they allow the child to spend enough time on the activity they chose. In some cases, the child may be working on their activity independently. In other cases, they may team up with a couple of other students who share their curiosity over that particular subject or activity. Together as a team, they discover, learn and grow through exploration. In a Montessori classroom, this means you won't find a teacher hurrying a child through a piece of work or putting time constraints on their exploration of a concept. It also means you aren't likely to find the whole group learning the same thing at the same time.
- The absorbent mind - A young child is naturally an eager, highly capable learner who can absorb a significant amount from their surroundings. That is why their preschool and early elementary years are such a critical time to expose them to as many experiences, concepts and lessons as possible. The ideal time to enroll a child in a Montessori program is during their toddler phase, anywhere from 16-32 months. Although learning is a life-long concept, the brain of a toddler is similar to a sponge, it soaks up everything in its path. There is no better time to begin encouraging their natural inclination to explore the world around them.
- Sensitive periods - Montessori pedagogy believes there are certain periods during which children are more ready to learn certain skills. These are known as sensitive periods, and last only as long as it is necessary for the child to acquire those skills. Many parents don't realize their child’s growth takes place across 4 scientifically based stages or planes, of development and each of these stages has different needs within the learning cycle. So, rather than adapting a subject to "fit" a certain age or stage, the Montessori theory says the educational approach itself is what should change to suit each stage. Through observation, Montessori teachers must identify sensitive periods in their students and provide the resources for children to flourish during this time.
- Prepared environment – The Montessori method suggests that children learn best in an environment that has been prepared to enable them to do things for themselves. Always child-centered, the learning environment should promote freedom for children to explore materials of their choice. Teachers should prepare the learning environment by making materials and experiences available to children in an orderly and independent way.
- Independence and Discovery - Montessori also recognizes each child is different, and therefore their interests and educational needs will vary, as well. We emphasize an individual approach that allows teachers to figure out and develop activities and learning experiences that follow each child’s specific needs and readiness. Over time, these principles foster self-esteem, independence, exploration and creativity; the keys to ultimately promoting joy and a love of learning and thus auto education.
Role of the teacher:
Teachers are a vital part of the Montessori classroom, but their role is different from what you might be accustomed to in a traditional school. In a traditional setting, you’ll find a teacher sharing facts and instructions at a rapid pace. Their role is to hand out information to their students and encourage them to memorize it. Teaching in this manner can often turn the joy of learning into a chore for children, taking away the fun of discovery.
In the Montessori environment, the teacher’s role is to encourage children’s natural ability to discover and create. The Montessori approach recognizes children learn best when teachers encourage them to use their natural creativity and intelligence to gather information and make discoveries. Their reward is the feeling of pride they get when they master a new concept.
A Montessori teacher is a facilitator, not a lecturer. A Montessori teacher plans activities designed to introduce and reinforce concepts. These are chosen based on the ages and abilities of the students in the class and often take a hands-on approach to learning. Once the child chooses their activity, the teacher then assumes the role of a guide, without becoming an obstacle nor inserting themselves too much into the natural learning process, leading the student into discovery. Montessori teachers manage classroom behaviors by modelling ongoing respect for all children and their work, by observing and using sensitive periods, interests and abilities to plan activities and by diverting inappropriate behavior to meaningful tasks.
The Montessori Curriculum
From birth to 3 years old (Toddler)
The foundations for the child’s future development are set during his/her first three years of life. Montessori calls this period the one of a “spiritual embryo”, in which the child does in the psychological sphere what the embryo did in the physical sphere. This process is achieved thanks to the child’s “absorbent mind”, which incorporates experiences, relations, emotions, images, language and culture through his/her senses and by the simple fact of living. These life experiences shape his/her brain, forming networks or neurons that have the potential of staying with the person for all his/her life. In this period from birth to 3 years old, the Montessori education concentrates in the development of speaking, coordinated movement and independence, which gives the child confidence, and allows him/her to discover his/her own potential and his/her place within a community.
From 3 to 6 years old (Primary)
The classroom curriculum for children from 3 to 6 years old is divided into four working areas:
- Practical Life: These are activities that aim to the care of the person, of others and of the physical environment where they live in. These activities include tasks that are familiar to the child: washing, polishing, setting the table, arranging flowers, etc. They also include activities of "grace and courtesy", which are part of all civilized people. Through these and other activities, children achieve coordination and control of movement and exploration of his/her surroundings. Children learn to complete a task from beginning to end, they develop their will, self-discipline, the capacity of concentration and self-confidence.
- Sensorial: Children at this age learn through senses more than through their intellect. The sensorial materials are tools for children to refine each of their senses. Each material isolates a specific quality: smell, size, weight, texture, flavor, colour, etc. In this preschool age, when children are "bombarded" with sensorial information, these materials allow them to find order and meaning to the world, raising his/her capacity of perception, favoring observation and a sense of admiration for everything that surrounds him/her.
- Language: When the child enters a Montessori class at age 3, they enrich the language that they had already acquired. They are capable of using it intelligently with precision and beauty, slowly realizing its properties. They learn to write, starting with their senses (hearing and touching), and as a natural consequence they learn to read. As an extension of language activities, children learn about geography, history, art and music. These areas help the child to know his/her surroundings and to realize the place the child occupies in this world. They teach him to respect and love for his/her environment, and they create a sense of solidarity with all humanity and his/her habitat.
- Mathematics: The materials help the child to learn and understand mathematical concepts when working with concrete materials that lead him/her intuitively to abstract concepts. They offer him/her sensorial impressions of the numbers and set the foundations for algebra and geometry.
Advantages of Montessori education:
- Enthusiastic self-motivated learners
- Improved social and problem-solving skills
- Advance understanding of abstract mathematical concepts and outstanding reading abilities
- Compassion, high self-esteem and good manners

